Discover the Power of Virtual Reality for Immersive Experiences
In recent years, Virtual Reality (VR) has emerged as one of the most transformative technologies, reshaping how we interact with the digital world. This article explores the incredible potential of VR in various sectors and its applications, benefits, challenges, and prospects while uncovering its immersive experiences.
Introduction to Virtual Reality (VR):
Virtual Reality is a computer-generated environment that immerses users in a simulated world, allowing them to interact with their surroundings in real-time. The experience can be so compelling that users often feel like they are truly “inside” this virtual space, disconnected from the physical world.
The history of VR can be traced back to the 1960s. The first virtual reality systems, such as the Sensorama and the Sword of Damocles, were rudimentary. Fast forward to today, advancements in technology have significantly improved the quality and accessibility of VR, making it an integral part of various industries. This article will explore how VR works, its applications across different fields, its benefits and challenges, and its exciting future.
How Virtual Reality Works
Key Components of Virtual Reality: Hardware and Software
To grasp how VR operates, it’s crucial to understand its main components.
- VR Headsets: At the core of VR technology, headsets like the Oculus Rift, HTC Vive, and PlayStation VR provide a gateway into virtual worlds. These devices feature high-resolution displays, motion sensors, and built-in audio systems, creating a sensory experience that mimics Reality.
- Controllers: Controllers are essential for interacting with virtual environments. They translate the user’s physical movements into the digital realm, allowing for actions like grabbing objects, pressing buttons, and navigating menus.
- Tracking Systems: Advanced tracking systems use infrared, cameras, or external sensors to monitor the user’s movements and adjust their perspective in real time. This tracking gives users the impression that they are actually in the virtual environment.
Types of Virtual Reality:
Immersive, Semi-Immersive, and Non-Immersive are some known classifications of Virtual Reality.
There are several types of VR experiences, each offering a different level of immersion:
- Immersive VR: This type offers complete immersion in a virtual environment, where users are entirely cut off from the real world. Users can interact with their surroundings through head and body movements.
- Semi-immersive VR: In semi-immersive VR, users experience a 3D environment while being aware of their surroundings. This form is often used in educational settings where full immersion isn’t necessary.
- Non-Immersive VR: Non-immersive VR is viewed on traditional screens and lacks the sensory engagement of immersive VR. While it can still be engaging, it doesn’t provide the same level of interaction.
Applications of Virtual Reality:
The versatility of Virtual Reality has led to its implementation in numerous sectors, each reaping the benefits of its immersive capabilities.
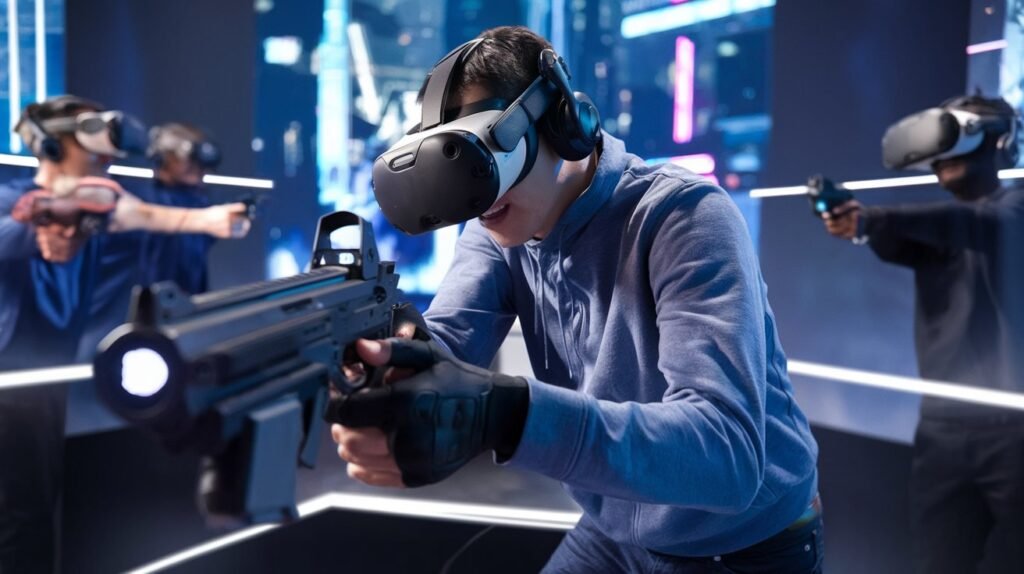
Virtual Reality in Gaming:
One of the most significant impacts of VR has been in the gaming industry. VR games provide players with unprecedented levels of engagement, allowing them to experience adventures from a first-person perspective. Popular titles like “Beat Saber” and “Half-Life: Specifically, “Alyx” present how VR can change gaming, which provides fun and exercises as players get up and use their bodies.
VR in Education and Training:
Virtual Reality is changing the way students are taught through rich and real interaction that cannot be attained through conventional teaching methods. For example, VR can transport students to historical sites, allowing them to explore ancient civilizations as if they were actually there. In medical training, students can practice surgical procedures in a risk-free environment, gaining valuable experience before working with real patients.
VR in Healthcare: Therapy and Surgery:
In the healthcare sector, VR is being used for therapeutic purposes, such as exposure therapy for phobias and post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD). By simulating real-world scenarios in a controlled environment, patients can confront their fears gradually and safely. Additionally, VR simulations are used in surgical training, enabling doctors to practice complex procedures without jeopardizing patient safety.
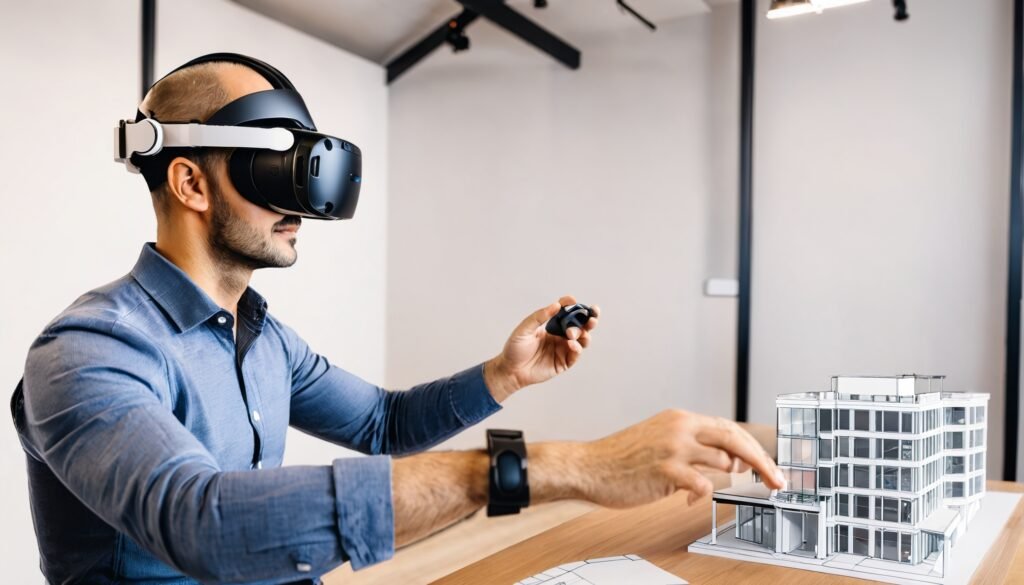
Virtual Reality in Architecture and Design:
Architects and designers harness VR to create interactive models of buildings and spaces. Clients can walk through these virtual models, providing feedback and making changes before construction begins. This enhances client satisfaction and reduces costly modifications during the building process.
VR in Tourism and Travel:
The tourism industry has embraced VR technology to offer virtual tours of destinations, allowing potential travelers to explore places before booking trips. From virtual strolls through the streets of Paris to exploring the Great Barrier Reef, VR provides an engaging way to promote travel experiences.
Benefits of Virtual Reality:
Enhanced Learning Experiences:
One of the most significant advantages of VR is its ability to enhance learning experiences. By immersing students in interactive environments, they can retain information more effectively. Studies have shown that immersive learning can lead to higher engagement and better academic performance.
Realistic Simulations and Training:
It effectively offers real-world use in almost any aviation, defense, or medicine sector. Trainees can make mistakes, but there is no danger for the company/hospital or patients on a computer. This hands-on experience leads to better preparedness when facing real challenges.
Entertainment Revolution: Movies and Gaming:
Virtual Reality is revolutionizing gaming and how consumers experience movies and other related forms of entertainment. With VR, viewers can step into their favorite films, making them active participants in the story rather than passive spectators. This shift in engagement can lead to a more memorable and enjoyable experience.
Challenges and Limitations of VR:
Despite its numerous benefits, Virtual Reality faces challenges that may hinder its widespread adoption.
High Costs of VR Equipment:
One of the most important issues that might potentially astound many consumers is the Cost of great VR devices. While prices have decreased, premium headsets and systems still require a substantial investment, making them inaccessible for some users.
Technical Challenges: Lag, Resolution, and Graphics:
Current VR systems can encounter technical issues such as latency, low resolution, and graphics limitations. Any lag between a user’s movements and the VR display can break immersion and disorient the experience.
Health Concerns and Side Effects of VR Use:
Prolonged use of VR can cause various health issues, including eye strain, headaches, and motion sickness. These health concerns must be addressed, especially as VR becomes more integrated into everyday life.
Positive & Negative Effects of Virtual Reality on Human Life:
Positive Effects:
Virtual Reality (VR) offers significant positive effects, such as enhanced learning experiences, improved training for skills, and therapeutic applications for mental health conditions. It fosters empathy by allowing users to experience different perspectives and promotes social interaction in virtual environments.
Negative Effects:
However, there are also negative effects, including physical discomforts like eye strain and motion sickness, potential isolation from real-life connections, and the risk of addiction. Furthermore, excessive exposure to virtual violence can lead to desensitization, while the high costs of VR technology may create accessibility issues. Balancing these aspects is crucial as VR continues to evolve.
Future of Virtual Reality:
Predictions for the VR Industry:
Experts predict that Virtual Reality will continue to grow and evolve, integrating into more aspects of our daily lives. As technology advances, VR systems will become more affordable, user-friendly, and sophisticated, increasing industry adoption.
Emerging Trends in Virtual Reality:
Several emerging trends are shaping the future of VR, including the rise of social VR, where users can interact in virtual spaces, and the incorporation of haptic feedback technology, allowing users to “feel” their virtual environments. These innovations will enhance the sense of presence and realism in VR experiences.
The Role of Artificial Intelligence (AI) in Enhancing VR Experiences:
Artificial Intelligence is playing an increasingly significant role in the VR landscape. AI can personalize experiences by adapting environments based on user preferences and actions. This capability makes VR more engaging and tailored to individual users, enhancing overall satisfaction.
Conclusion:
The power of Virtual Reality to create immersive experiences is truly remarkable. From gaming and education to healthcare and architecture, VR is reshaping how we interact with the world. While there are challenges to overcome, the future of VR is promising, with endless possibilities for innovation and enhancement. As we continue to explore and develop this technology, we can expect to see its influence grow, enriching our lives and providing unique experiences we have yet to imagine.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs):
What industries use Virtual Reality?
VR is utilized across multiple industries, including gaming, education, healthcare, architecture, and tourism, enhancing experiences and engagement.
How does Virtual Reality enhance learning?
VR creates immersive environments that engage students, making complex subjects easier to understand and retain, leading to improved learning outcomes.
Can VR be harmful to health?
While VR is generally safe, prolonged use can cause eye strain, dizziness, and motion sickness. It’s essential to take breaks and use VR responsibly.
What is the potential of Virtual Reality in the future?
The future of VR looks promising, with advancements in technology expected to make VR more accessible and integrated into everyday life.
How accessible is VR for the average consumer?
Although VR equipment costs have decreased, high-quality systems can still be expensive. Although such facilities are beyond the reach of so many people, some signs that improved options will soon be accessible.
What is the difference between VR and AR?
While Virtual Reality drops users into an entirely simulated experience, Augmented Reality is the technology that puts interactivity over a live video feed.